Location: Kelappaji College of Agricultural Engineering and Technology, Tavanur Function: The scheme was formulated to conduct feasibility tests on farm implements and machinery under various agro-climatic conditions with the following objectives:
- To identify the present farm mechanization gaps and future needs for improved farm equipment on the basis of objective analysis of prevailing agro-socio-economic factors for different crops, cropping patterns and agro-climatic regions.
- To conduct feasibility testing on farmers’ field of prototypes of proven designs of farm implements and machinery, selected from different regions for adoption under local conditions with a view to bridge the identified mechanization gaps.
- To educate the farmers about the usefulness of the improved implements and their efficient handling by front line demonstrations.
Identifying Research Problem and their prioritization
Studies are conducted periodically on problems on agricultural sector for formulation of research priority in different agro climatic regions. The research priorities are made on the basis of comments and suggestions from the farmers, agricultural officers, engineers from the department of agriculture and scientists of different regions including problematic areas
Salient Accomplishments
Study on Paddy seeder for pre- germinated seeds
Broadcasting of paddy during pre-monsooon showers (May) is practiced in Palakkad district for first crops season and transplanting is followed in the puddle soil for second and summer seasons. Due to scarcity of water, a machine for sowing paddy seeds in the puddled soil is introduced.

Study on Paddy seeder for dry sowing
For establishing good quality crop with the available soil moisture power operated seeders was introduced.
Evaluation of Mini tiller with attachments for plantation/ horticultural crops
The mini tillers with attachments is found useful for the horticultural and plantations crops like coconut, arecanut, banana, pepper, cashew nut, rubber, vanilla etc. which are being grown as high intensity crops in inter cropping, multi cropping and multi storied cropping systems under homestead agriculture.

Rotavator for plantation/ horticultural crops
Rotovators of power tillers and tractors are commonly used for paddies but not popular in plantation/ horticultural crops. Introduction of rotavator for non conventional crops reduced cost of cultivation and improved income.

Study on power operated Coconut dehusker
Husking of coconuts is carried out manually using the traditional crow-bar type tool. It needs great skill and the operation is highly dangerous and laborious. Youngsters are not ready to take up the job and scarcity is felt throughout the state. A 3 HP motor operated coconut dehusker was developed and evaluated.
Study on Coconut and arecanut palm tree climbers
Study on Tractor mounted pulverising roller
Study on self propelled hydro tiller

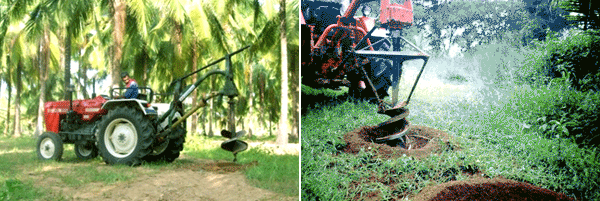
Study on tractor operated post hole diggers
The tractor operated JNP, FII and Gomadhi makes of post hole diggers having auger diameter with 150, 180, 220, 300, 450 and 600 mm were evaluated in different soil conditions. Farmers used the post hole diggers to make pits suitable for planting coconut, areca nut, rubber seedlings, planting banana suckers and also for erecting fencing pillars. Damages to the central tip and the double starting edges were noted in laterite soils. Portable engine operated hole diggers were also used for planting many horticultural, plantation, medicinal and ornamental seedlings in the laterite soils.
Study of self propelled rice transplanter
Ten types of transplanters were evaluated. They are: IRRI 5-row transplanter, IRRI 6-row transplanter, APAU power tiller mounted 8-row transplanter, Improved tiller mounted transplanter (KAU) and Chinese Yanji 8-row transplanter, Walk behind transplanterKukje, AIC, Tong-Yang, Four wheel Yanmar and LG transplanters. The method of mat seedling preparation was standardized to suit different agro-ecological conditions. Trainings were given to the dealers and field operators regarding the improved mat preparation method and transplanting. Feasibility trials and extensive transplanting in the farmers fields were done in four districts. Savings of 80% labour, 56% cost, 40% time and 30% seed paddy were obtained. An increase in yield up to 18% compared to manual transplanting was also noted. Few hundred rice transplanters are successfully used in Kerala.

Evaluation of mini paddy combine harvester
The following 13 makes of the combine harvesters were evaluated. They are: Mitsubishi 18 hp mini combine, Kukje 18 hp head feed combine, Kukje 35 hp head feed combine, Kubota 48 hp rice combine, Claas Crop Tiger 54 hp grain tank combine, Kukje DKC-515 50 hp hopper combine, Kukje DKC-685 64 hp tank combine, Tractor 60 hp wheel type combine, Swaraj 55 hp crawler type combine, Preet 60 hp crawler type combine, Dae-Dong head feed combine, Redlands Champion TRF-15 combine, and Kubota DC 68G combine. The ChineeseSifang mini combine was also evaluated for the first time and was found to perform unsatisfactorily due to failure of its different components. Wheel type combine harvesters were found not suitable, because of traction problem, where as the track type combines worked well even in muddy field. The Dae-Dong head feed combine was introduced first time in Kerala during March 2010. It was evaluated in two seasons in four locations and was found to perform better compared to other combines in the highly sinking fields with heavy weed infestation.

Study on tractor operated zero till seed drill
The tractor operated zero till seed drill was evaluated for seed rate, field capacity and fuel consumption. The fluted roller mechanism was calibrated to get the maximum field performance. The agronomically recommended seed rate for cow pea, green gram and paddy are 50-60 kg/ha, 20-25 kg/ha, and 80-90 kg/ha, respectively, where as the seed rate obtained during performance evaluation were 58.71 kg/ha, 22.53 kg/ha and 74.75 kg/ha. The field capacity obtained were 0.426 ha/h, 0.409 ha/h and 0.393 ha/h respectively and the fuel consumption were 0.390 l/h, 0.362 l/h and 0.365 l/h, respectively. The line sowing improved the yield and made weeding easier. The soil moisture available after the paddy harvest was utilized for seed germination and growth till the onset of summer paddy. Improvement of seed metering mechanism is needed for sowing summer paddy